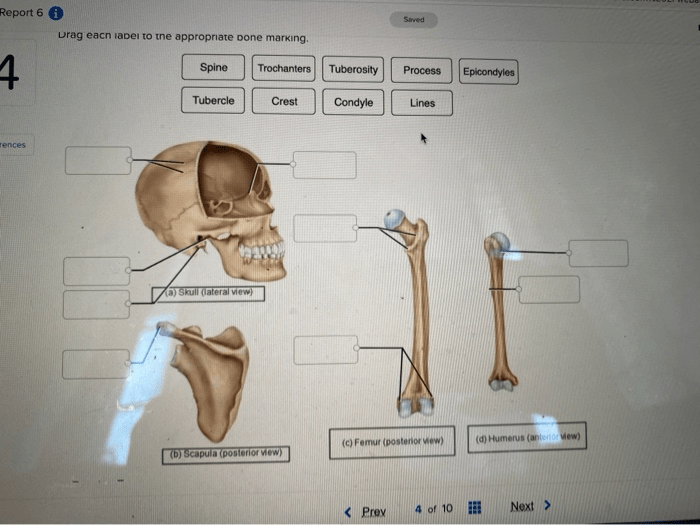
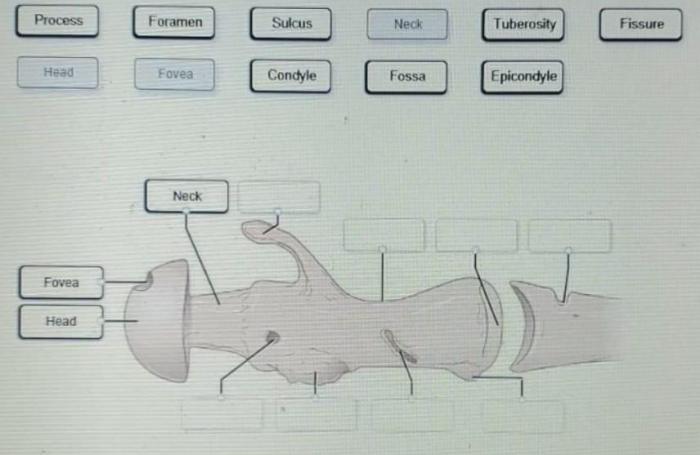
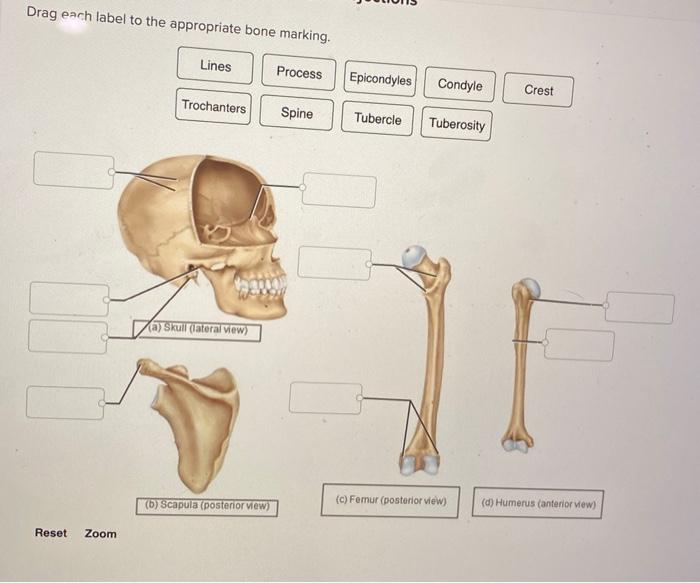
Drag each label to the appropriate bone marking introduces readers to the intricate world of human anatomy, where bone markings play a pivotal role in defining the structure and function of our skeletal system. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of bone markings, their diverse types, and their clinical applications, providing a foundational understanding for students, medical professionals, and anyone fascinated by the human body.
Bone Markings Overview: Drag Each Label To The Appropriate Bone Marking
Bone markings are anatomical features found on the surface of bones. They serve various functions, such as providing attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons, facilitating joint movement, and protecting delicate structures within the bone.
Bone markings are classified into several types based on their shape, size, and function. Some common types include:
- Projections: These are bony extensions that provide attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
- Depressions: These are indentations or cavities that house or protect structures like blood vessels, nerves, or joints.
- Foramina: These are holes or openings that allow nerves, blood vessels, or other structures to pass through.
- Canals: These are tunnels or channels that run through the bone and provide passage for nerves, blood vessels, or tendons.
Drag-and-Drop Exercise
Goal: To identify and match different bone markings with their corresponding descriptions.
Instructions:
- Drag the bone marking labels from the left column to the appropriate descriptions on the right.
- Once all bone markings are correctly matched, click the “Submit” button to check your answers.
Bone Marking Categories
| Bone Marking | Description | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Projections | Bony extensions that provide attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons. | Various | Muscle attachment, joint movement |
| Depressions | Indentations or cavities that house or protect structures like blood vessels, nerves, or joints. | Various | Protection, cushioning |
| Foramina | Holes or openings that allow nerves, blood vessels, or other structures to pass through. | Various | Passage of nerves, blood vessels |
| Canals | Tunnels or channels that run through the bone and provide passage for nerves, blood vessels, or tendons. | Various | Passage of nerves, blood vessels, tendons |
Common Bone Markings, Drag each label to the appropriate bone marking
- Tendon: A tough, fibrous cord that attaches muscle to bone.
- Ligament: A tough, fibrous band that connects bone to bone.
- Articular surface: A smooth, cartilage-covered surface that forms part of a joint.
- Epiphysis: The end of a long bone.
- Diaphysis: The shaft of a long bone.
Regional Bone Markings
Different regions of the skeleton have specific bone markings that reflect their function.
For example, the skull has numerous foramina for the passage of nerves and blood vessels. The long bones of the limbs have prominent projections for muscle attachment and articular surfaces for joint formation.
Clinical Applications
Bone markings are important in clinical practice.
- They can be used to identify and locate anatomical structures during surgery.
- They can help diagnose fractures and other bone injuries.
- They can be used to assess bone health and identify conditions like osteoporosis.
FAQ Summary
What are bone markings?
Bone markings are anatomical features found on the surface of bones that serve various functions, such as providing attachment points for muscles and ligaments, facilitating joint movement, and protecting underlying structures.
How many types of bone markings are there?
There are numerous types of bone markings, each with its unique characteristics and functions. Some common types include processes (projections), foramina (holes), fossae (depressions), and trochanters (large processes found near joints).
What is the clinical significance of bone markings?
Bone markings are crucial for medical diagnosis and treatment. By examining bone markings, healthcare professionals can assess bone health, identify fractures or abnormalities, and plan surgical interventions. Bone markings also provide guidance for injections, nerve blocks, and other medical procedures.